FDA Requirements: What You Need to Know About Drug Safety and Labeling
When you pick up a prescription, the FDA requirements, the set of rules the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enforces to ensure drugs are safe, effective, and properly labeled. Also known as drug approval standards, these rules dictate everything from how a medicine is tested to how its side effects are explained to you. This isn’t bureaucracy—it’s your protection. The FDA doesn’t just approve drugs; it tracks them after they hit the market, forces updates when new risks appear, and now even pushes for simpler, clearer patient information.
FDA requirements cover more than just what’s in the pill. They control how warnings are written, how pharmacies hand out instructions, and even how generic drugs prove they work the same as the brand name. For example, if a drug like DPP-4 inhibitors, a class of diabetes medications that can rarely cause severe joint pain starts showing new side effects, the FDA requires the manufacturer to update the label and alert doctors and patients. That’s why you see those safety alerts in the news. Same goes for patient medication information, the new one-page summary the FDA is rolling out to replace confusing, inconsistent Medication Guides. It’s meant to tell you what you actually need to know: what the drug does, what to watch for, and when to call your doctor.
These rules also shape how you interact with your meds. If you’re on blood thinners, FDA requirements force manufacturers to clearly warn about interactions with herbal supplements like Ginkgo Biloba, a common supplement that can dangerously increase bleeding risk. If you’re older and taking five or more drugs, FDA requirements push for deprescribing guidelines so doctors don’t just keep adding pills—they start cutting the ones that aren’t helping anymore. Even how your insurance puts drugs into tiers? That’s tied to FDA approval status and safety data.
What you’ll find here isn’t a list of legal jargon. It’s real stories from people who learned the hard way that inactive ingredients can trigger allergies, that drug interactions hide in plain sight, and that what’s on the label might not tell you the whole story. You’ll see how FDA requirements protect you—and where they fall short. You’ll learn how to read between the lines of a medication guide, spot when a warning is being ignored, and ask the right questions before you swallow a new pill. These aren’t abstract rules. They’re the reason your doctor knows not to mix certain drugs, why your pharmacist asks if you take ginkgo, and why your next prescription might come with a one-page summary that actually makes sense.
Bioequivalence Studies: What the FDA Requires Generic Drug Manufacturers to Prove
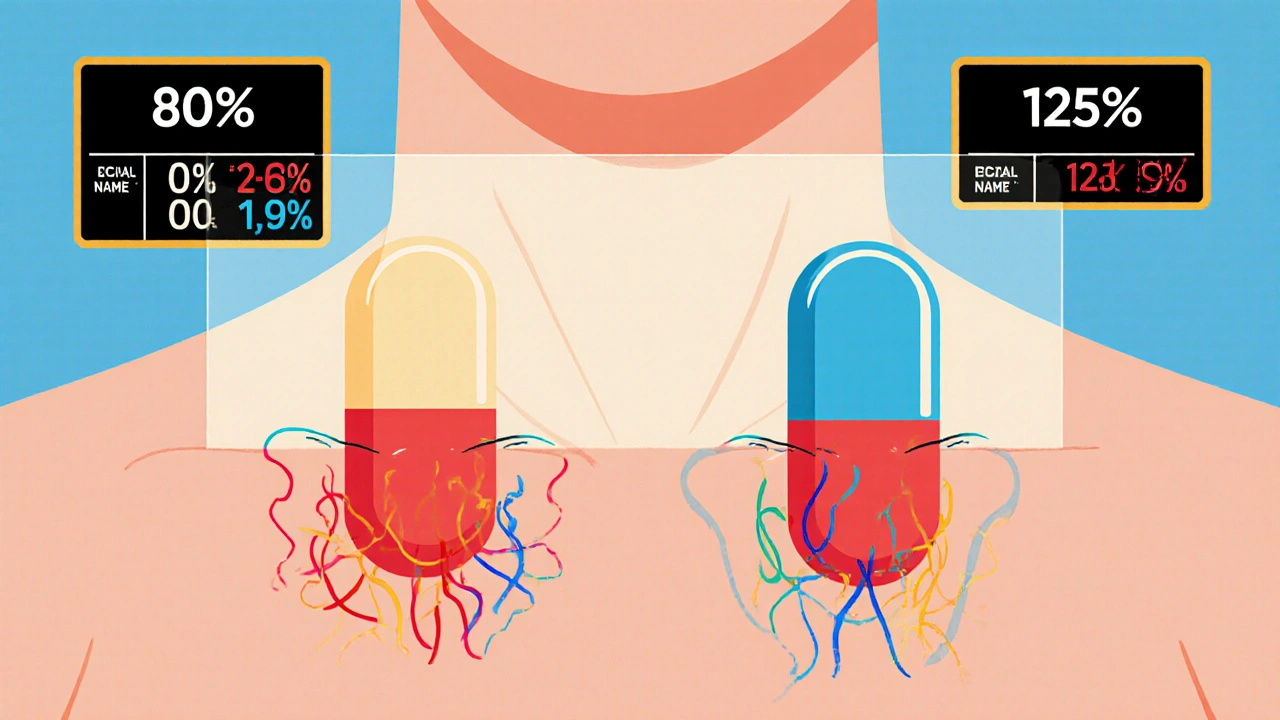
The FDA requires generic drug manufacturers to prove bioequivalence through rigorous studies showing their product absorbs at the same rate and extent as the brand-name drug. Learn the 80/125 rule, biowaivers, NTID exceptions, and why this matters for patient safety.
- November 27 2025
- Tony Newman
- 12 Comments
