Generic Medicines and Drug Safety in November 2025: What You Need to Know
When it comes to generic medicines, affordable versions of brand-name drugs that must meet the same safety and effectiveness standards as the original. Also known as generic drugs, they make up over 90% of prescriptions in the U.S. because they work the same way—but only if they pass strict testing. That’s where bioequivalence studies, rigorous tests that prove a generic drug absorbs into your body at the same rate and level as the brand-name version. Also known as bioequivalence criteria, these studies are required by the FDA before a generic can be sold. If a generic doesn’t meet the 80/125 rule—meaning its absorption falls within 20% of the brand—it doesn’t get approved. This isn’t just paperwork; it’s what keeps you safe when you switch from a name-brand pill to a cheaper one.
But safety doesn’t stop at absorption. medication interactions, when two or more drugs, supplements, or even foods affect each other in harmful ways. Also known as drug combos, these can turn a routine treatment into a life-threatening event. In November, we highlighted deadly pairs like opioids with alcohol, or benzodiazepines with sleep aids. Even natural products like Ginkgo Biloba, a popular herbal supplement often taken for memory. Also known as ginkgo, it can dangerously boost bleeding risk when mixed with blood thinners like warfarin or aspirin. And it’s not just what you take—it’s what you don’t. Many people keep taking drugs they no longer need. That’s where deprescribing, the planned, safe reduction of unnecessary medications, especially for older adults on multiple pills. Also known as medication review, it’s not about quitting drugs cold turkey—it’s about smart, step-by-step cuts to reduce side effects and improve quality of life. One post showed how simple habits like walking more or sleeping better can lower your need for meds without ditching your prescriptions.
Understanding your insurance formulary tiers, spotting the difference between a side effect and a real allergy, and knowing when to question a drug’s necessity—all these are part of taking control of your health. In November, we broke down how Tier 1 drugs cost less because they’re preferred by insurers, why single-source drugs can be way more expensive than multi-source ones, and how to read FDA alerts before they hit the news. You don’t need a medical degree to protect yourself. You just need to know what questions to ask. Below, you’ll find clear, no-fluff guides on exactly that: how to read your pills, avoid dangerous mixes, save money on prescriptions, and speak up when something doesn’t feel right.
Active vs Inactive Drug Ingredients: Why the Difference Matters for Your Health
Active ingredients treat your condition, but inactive ingredients can cause side effects, trigger allergies, or even affect how well your medicine works. Know what’s really in your pills.
- November 28 2025
- Tony Newman
- 15 Comments
Bioequivalence Studies: What the FDA Requires Generic Drug Manufacturers to Prove
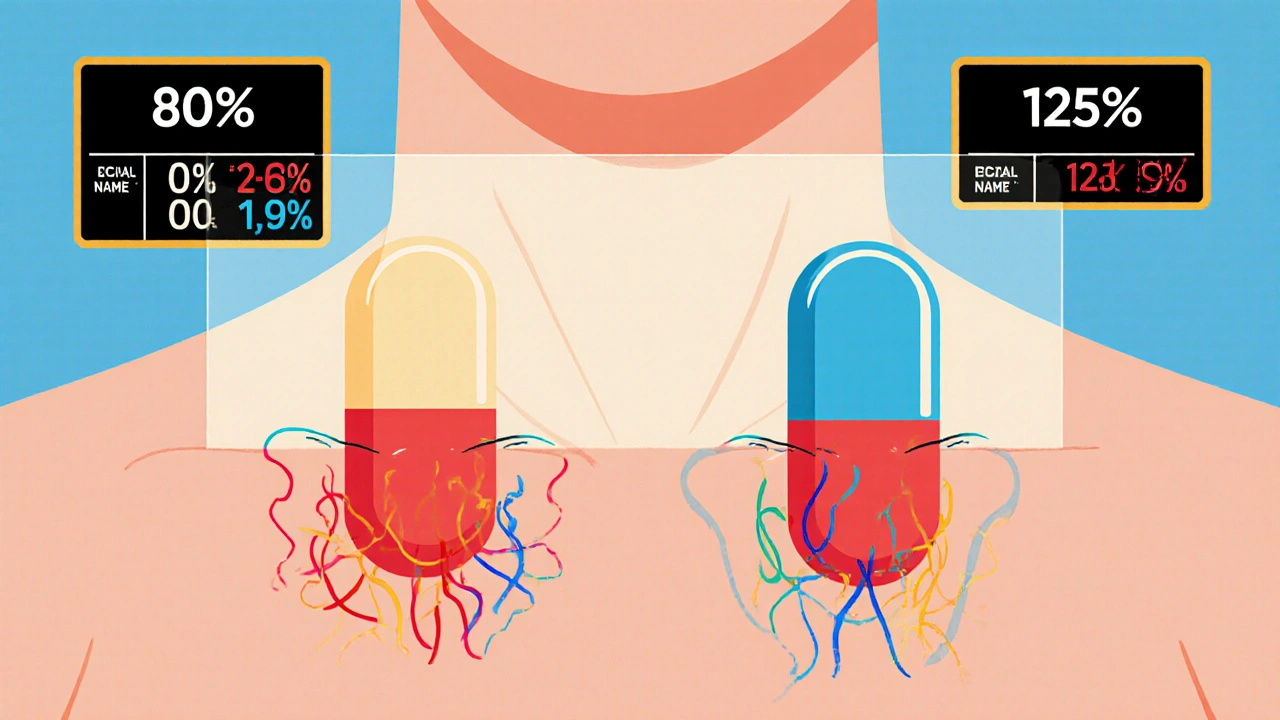
The FDA requires generic drug manufacturers to prove bioequivalence through rigorous studies showing their product absorbs at the same rate and extent as the brand-name drug. Learn the 80/125 rule, biowaivers, NTID exceptions, and why this matters for patient safety.
- November 27 2025
- Tony Newman
- 12 Comments
Insurance Formulary Tiers Explained: Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3, and Non-Formulary Drugs

Understand how insurance formulary tiers work-Tier 1 to Tier 5 and non-formulary drugs-and how they affect your out-of-pocket costs for prescriptions. Learn what drives tier placement and how to save money.
- November 26 2025
- Tony Newman
- 10 Comments
Red Flag Drug Combinations to Avoid for Safer Treatment

Certain drug combinations can be deadly, even when used as prescribed. Learn the most dangerous pairs - like opioids with alcohol or benzodiazepines - and how to protect yourself from hidden, life-threatening interactions.
- November 25 2025
- Tony Newman
- 16 Comments
Clotting Disorders and Anticoagulation: Understanding INR, DOACs, and Safety

Learn how INR monitoring and DOACs work for clotting disorders, their safety profiles, cost differences, and who should use each type of blood thinner. Understand real-world risks, benefits, and the latest guidelines.
- November 24 2025
- Tony Newman
- 15 Comments
Caffeine Cutoff Times: When to Stop Coffee for Better Sleep

Learn the science-backed caffeine cutoff times to improve sleep onset and quality. Discover when to stop coffee, energy drinks, and hidden caffeine sources for deeper, more restful sleep.
- November 23 2025
- Tony Newman
- 9 Comments
How to Tell a Side Effect from a True Drug Allergy
Learn how to tell the difference between a harmless side effect and a dangerous drug allergy. Most reactions aren’t allergies-mislabeling them can limit your treatment options and put your health at risk.
- November 22 2025
- Tony Newman
- 17 Comments
Single-Source vs Multi-Source Drugs: What Patients Need to Know About Cost, Effectiveness, and Choices

Understand the difference between single-source and multi-source drugs to save money and make smarter choices. Learn how pricing, generics, and insurance affect your out-of-pocket costs.
- November 21 2025
- Tony Newman
- 17 Comments
Antihistamines: First-Generation vs. Second-Generation Compared

Learn the key differences between first- and second-generation antihistamines - from how they work and their side effects to which one is better for daily use, sleep, or sudden allergies.
- November 20 2025
- Tony Newman
- 11 Comments
Hyperparathyroidism: High Calcium, Bone Loss, and When Surgery Is Necessary
Hyperparathyroidism causes high calcium, bone loss, and chronic fatigue. Surgery is the only cure. Learn the signs, when to act, and what to expect after treatment.
- November 20 2025
- Tony Newman
- 12 Comments
